The Science of Water Hardness: Calcium, Magnesium and More

Water is essential for our daily lives, and we often take its quality for granted. But have you ever noticed that some water feels different than others? It’s not just your imagination. Water hardness, influenced by minerals like calcium and magnesium, plays a significant role in how water behaves and its impact on our appliances, skin, and more. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the science of water hardness, exploring its causes, effects, and solutions. Get ready to unravel the mysteries of your tap water!
Understanding Water Hardness
What is Water Hardness?
Water hardness refers to the concentration of minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium ions, in your water. It’s typically measured in parts per million (ppm) or grains per gallon (gpg). The higher the concentration, the harder the water.
Causes of Water Hardness
Water becomes hard as it passes through geological formations, picking up minerals from rocks and soil. The main culprits are calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium carbonate (MgCO3).
Effects of Hard Water
On Your Plumbing
Hard water can wreak havoc on your plumbing system. The minerals in hard water can build up in pipes, leading to clogs and reduced water flow. This buildup, known as scale, can be a costly problem.
On Your Appliances
Your appliances, such as dishwashers and water heaters, are not safe from the effects of hard water either. The scale can accumulate on heating elements, reducing efficiency and lifespan.
On Your Skin and Hair
Ever noticed dry, itchy skin or dull, lifeless hair after a shower? Hard water might be to blame. The minerals can leave residue on your skin and hair, making them feel less than stellar.
Measuring Water Hardness
Testing Water Hardness
You can determine the hardness of your water with a simple test kit or by sending a sample to a laboratory. It’s essential to know your water’s hardness level to address potential issues.
Degrees of Hardness
Water hardness is categorized into degrees: soft, moderately hard, hard, and very hard. The classification depends on the mineral concentration. Soft water has fewer minerals, while very hard water is loaded with them.
Dealing with Hard Water
Water Softeners
Water softeners are a popular solution for dealing with hard water. These devices use ion exchange to replace calcium and magnesium ions with sodium or potassium ions, effectively softening the water.
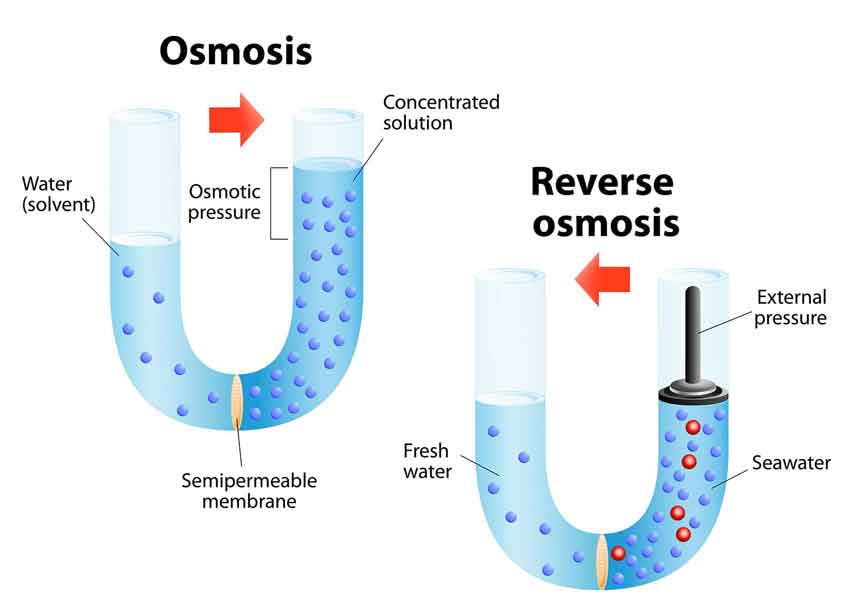
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis systems can remove minerals and contaminants from your water, providing a comprehensive solution for improving water quality.
Water Conditioners
Water conditioners alter the structure of minerals, preventing them from forming scale. They are a salt-free alternative to traditional water softeners.
Benefits of Softened Water
Appliance Longevity
By using a water softener, you can extend the lifespan of your appliances, saving you money in the long run.
Softer Skin and Hair
Enjoy smoother, healthier skin and hair by reducing mineral buildup with softened water.
Efficient Cleaning
Hard water can hinder the effectiveness of detergents and soaps. Softened water allows cleaning products to work their magic.
Water Hardness and Your Health
Is Hard Water Safe to Drink?
In most cases, hard water is safe to drink as it contains essential minerals. However, extremely hard water may have an unpleasant taste, leading people to prefer softened water for consumption.
Mineral Benefits
The minerals in hard water, such as calcium and magnesium, are essential for your health. They contribute to your daily intake of these nutrients.
Conclusion
Water hardness is not just an abstract concept; it affects our daily lives in numerous ways. From plumbing and appliances to our own well-being, understanding and managing water hardness is crucial. Whether you choose a water softener, reverse osmosis system, or water conditioner, taking action to address hard water can lead to a happier, healthier, and more efficient home.
FAQs About Water Hardness
1. Can hard water cause health problems?
While hard water itself is generally safe to drink, extremely hard water may have an unpleasant taste. It’s unlikely to cause health problems, and the minerals in hard water can even be beneficial.
2. How can I test the hardness of my water?
You can test the hardness of your water using a simple test kit or by sending a water sample to a laboratory for analysis. Knowing your water’s hardness level is essential for making informed decisions.
3. Are there natural ways to soften water?
Natural water softening methods, such as boiling or using a water filter, can reduce the concentration of minerals to some extent. However, for significant hardness reduction, you may need a water softener or reverse osmosis system.
4. Do I need a water softener if I have a water conditioner?
Water softeners and water conditioners serve similar purposes, but they use different methods. Water conditioners are salt-free and alter the mineral structure, while water softeners use ion exchange. The choice depends on your specific needs and preferences.
5. What are the signs that I have hard water?
Common signs of hard water include scale buildup on faucets and appliances, reduced water flow, and the feeling of dry skin and hair after bathing. If you notice these issues, it’s a good indicator that your water may be hard.